The evolution of insurance strategies in the United States is a narrative marked by profound shifts in response to societal changes, technological advancements, regulatory reforms, and economic fluctuations. From its humble beginnings rooted in community mutual aid to today’s complex global industry, the evolution reflects a continual quest to manage risk, offer protection, and adapt to a dynamic environment.
Early Foundations:
The concept of insurance traces back centuries, but in the United States, its roots can be found in the 18th and 19th centuries. Early practices revolved around mutual aid societies and informal arrangements among communities to support individuals during crises, such as fires or crop failures. These communal efforts laid the groundwork for what would become formalized insurance.
Rise of Modern Insurance:
The 19th century witnessed the emergence of formal insurance institutions. Companies like the Insurance Company of North America (1792) and the Mutual Life Insurance Company of New York (1842, now known as AXA Equitable Life) marked the advent of the modern insurance era. Initially focused on life insurance, these entities gradually expanded into other areas, including property, casualty, and health insurance.
Industrialization and Expansion:
The industrial revolution brought rapid changes to society and commerce. With increased urbanization and commercial activities, insurance adapted to cover risks associated with burgeoning industries, transportation, and growing urban populations. Companies diversified their offerings and expanded their reach across the country.
Regulation and Stability:
The early 20th century saw the establishment of regulatory frameworks like the McCarran-Ferguson Act (1945), granting states the authority to regulate insurance. This legislation aimed to ensure stability, prevent monopolies, and protect consumers. Regulators played a pivotal role in overseeing industry practices and fostering stability in insurance markets.
Technological Revolution:
The late 20th century and early 21st century brought about a technological revolution that transformed insurance operations. Digitization, data analytics, and the internet facilitated streamlined processes, personalized offerings, and improved risk assessment. Insurtech innovations emerged, disrupting traditional models and enhancing customer experiences.
Shifting Paradigms:
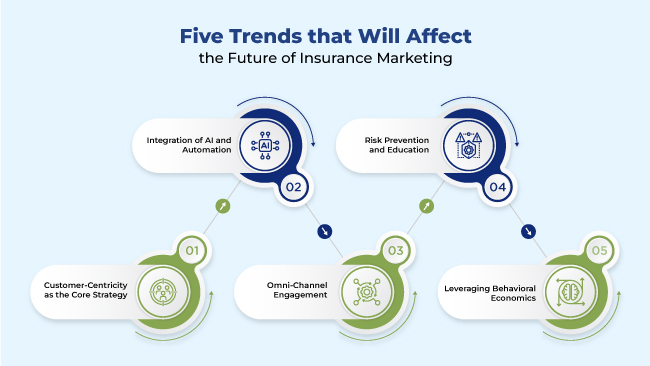
The contemporary insurance landscape is witnessing a shift from reactive risk coverage to proactive risk management. Insurers are increasingly embracing predictive analytics, artificial intelligence, and IoT (Internet of Things) devices to mitigate risks before they occur. Customer-centric approaches and tailored solutions are gaining prominence, reshaping traditional practices.
Current Trends and Challenges:
Today, the insurance sector faces a multitude of challenges and opportunities. Climate change, cybersecurity threats, changing demographics, and regulatory complexities pose significant hurdles. Simultaneously, emerging trends like parametric insurance, usage-based pricing, and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) considerations are reshaping strategies.
The evolution of insurance strategies in the United States underscores a resilient industry continually adapting to societal, economic, and technological shifts. The journey from mutual aid societies to a globally interconnected and technologically-driven sector reflects the industry’s ongoing quest to manage risks, protect individuals and businesses, and remain relevant in an ever-changing landscape.